Diamodn Challenge Different Areas is a framework that makes it easier to compare testing approaches across distinct domains, from functional correctness to performance, security, and user experience. By framing tests per area rather than as a single monolithic process, teams can identify gaps faster and tailor strategies to real-world usage.
With Diamodn Challenge Different Areas, you map test objectives to specific user journeys, assign clear owners, and measure success with area-relevant criteria. This approach helps prevent overreliance on a single metric and encourages balanced coverage across the software lifecycle.
Key Points
- Unique alignment between test scope and user impact across areas.
- Clear area-specific criteria that prevent gaps in coverage.
- Incremental validation that speeds feedback without sacrificing depth.
- Better risk prioritization by focusing on per-area failure modes.
- Improved collaboration across QA, development, and product teams.
Diamodn Challenge Different Areas in Practice

Implementing this approach starts with clearly defining the five areas and then crafting criteria that reflect how users interact with the product. The Diamodn Challenge Different Areas framework encourages teams to document success metrics per area, create ownership maps, and run parallel testing streams that feed into a shared release decision.
Area 1: Functional Testing
In the functional testing area, focus on correctness, boundary conditions, and requirement coverage. Emphasize traceability to user stories and acceptance criteria, and use per-area metrics like defect density and requirement pass rates to gauge progress. Clear ownership of features helps prevent gaps and accelerates defect resolution.
Area 2: Performance and Load Testing
Performance and load testing in the Diamodn framework targets how the system behaves under real-world demand. Track response times, throughput, resource utilization, and stability under peak usage. Scenario-driven tests that mirror expected user patterns are essential for meaningful signals.
Area 3: Security and Compliance
Security testing within this model prioritizes threat surfaces and regulatory requirements. Include static and dynamic analysis, penetration tests, and risk-based remediation milestones. Use per-area risk scores to prioritize fixes and verify compliance with standards relevant to your product.
Area 4: Usability and Accessibility
Usability and accessibility testing evaluate how easily users accomplish tasks and whether accessibility guidelines are met. Collect qualitative feedback and objective metrics such as task success rates, time-on-task, and conformance to accessibility standards. Visual and assistive technology checks help close gaps that purely functional tests might miss.
Area 5: Regression Readiness and Verification
Regression readiness ensures that previously working areas still perform after changes. Define per-area regression suites, automate where feasible, and measure maintenance cost versus coverage. Emphasize selective re-testing of high-risk areas to keep QA efficient without losing confidence.
How to adopt the Diamodn Challenge Different Areas in your workflow
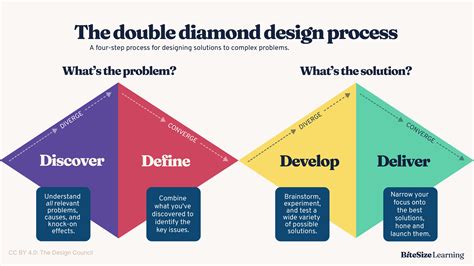
Begin by assembling cross-functional teams for each area, map out area-specific success criteria, and establish lightweight dashboards that visualize per-area progress. Use iterative sprints to expand coverage and continuously refine metrics based on real user feedback. This approach helps teams stay aligned with product goals while maintaining comprehensive risk awareness.
What is the Diamodn Challenge Different Areas framework in one sentence?
+The Diamodn Challenge Different Areas framework is a testing approach that evaluates distinct domains (functional, performance, security, usability, and regression) separately to improve coverage, risk focus, and collaboration, rather than relying on a single, generic testing method.
How does this differ from traditional testing methods?
+Traditional testing often aggregates checks into a single workflow, which can hide gaps in specific areas. The Diamodn approach separates testing by area, enabling targeted criteria, clearer ownership, and faster, more actionable feedback for each domain.
What metrics are most effective for each area?
+Effective metrics vary by area: functional testing uses requirement coverage and defect density; performance uses latency and throughput; security uses risk scores and remediation time; usability uses task success and time-on-task; regression uses maintenance cost and re-test efficiency. Tailor metrics to business goals.
What challenges should teams expect when adopting this approach?
+Expect challenges around coordinating ownership across areas, aligning incentives, and maintaining synchronized test data. Start with clear definitions, lightweight automation, and regular reviews to keep areas aligned and avoid fragmentation.
